Table of Contents
Types of Maintenance
The following figure represents the different types of maintenance.
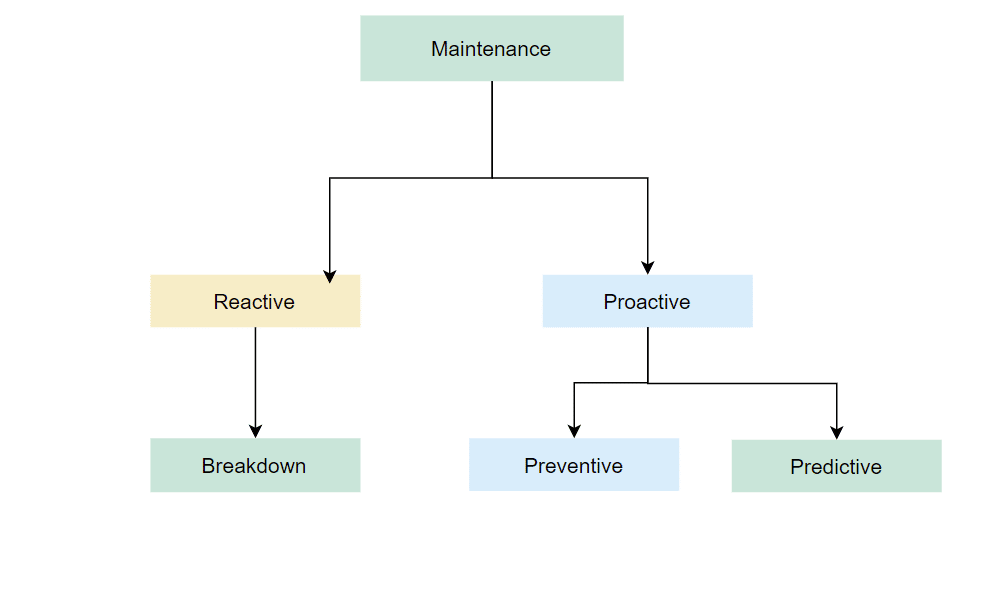
Breakdown or Reactive Maintenance
- Breakdown maintenance is one of the first and traditional Types of Maintenance which is carried out only when a machine fails to perform its function.
- A machine is allowed to operate up to its failure thus extracting the complete worthiness of a machine until it fails.
- It is an unplanned or sudden maintenance plan.
- It demands a large inventory of spare parts because it is unknown when and which component of a machine fails.
- This type of maintenance plan works well for a machine whose failure will not affect plant production. i.e., non-critical machines.
Preventive Maintenance
- Preventive maintenance is carried out before the failure of a machine.
- It is time-based maintenance.
- Maintenance activities are scheduled based on the calendar days.
- Machines are taken for maintenance even though there is no sign of functional failure.
- This type of maintenance plan works well for a machine that is not running continuously since preventive maintenance can be done only when the machinery is in off condition.
Drawbacks of Preventive Maintenance
- Since it is based on the calendar months, sometimes it is too early or too late for machine maintenance.
- There is a chance that minute damage in a component could be replaced early though it has a certain life left to function. I.e. Throwing the part away without utilizing its remaining useful life.
Predictive or Condition-based Maintenance
- It is a process of monitoring the present condition of a running machine i.e., a single or set of parameters of a machine is monitored that indicates a developing fault.
- Predictive maintenance is carried out only when there is an indication of a developing fault but it requires continuous monitoring of machine parameters.
- The time to failure of a machine can be estimated based on the parametric value trends or changes in the trends so that it can be planned for the next planned plant shutdown without leaving it to fail completely also time to failure represents the buffer time to purchase the spare parts.
- Predictive maintenance gives an early warning sign of a machine before it fails.
- Spare parts inventory is reduced.
Some of the commonly used predictive maintenance techniques in the industry are mentioned below.
- Acoustic Analysis
- Vibration Analysis
- Oil and Particle Analysis
- Infrared Thermography
- Non Destructive Test
- Ultrasound
Vibration monitoring/Analysis is a widely preferred condition-based monitoring technique to monitor the condition of rotating and reciprocating machinery. Almost all the faults like rotor imbalance, misalignment between driver and driven equipment, cavitation in a pump, bearing failure, cocked bearings, structural looseness, bent shaft, piping strain, soft foot, flow-induced vibrations, and rotor eccentricity…Etc can be easily detected by analyzing the vibration frequency and phase angle. Just a simple handheld portable vibration monitor is enough to check the vibration magnitude and periodic recordings of vibration magnitude represent the trend. By analysing the trend, incipient faults can be identified and catastrophic failures can be prevented.
Consider a centrifugal pump equipped with a mechanical seal handling a hazardous liquid. Assuming that shaft misalignment is responsible for the failure of the mechanical seal for instance.
- Periodic vibration monitoring will reflect the fault in terms of excess vibration magnitude at a certain frequency and phase angle. It comes under Predictive Maintenance.
- If the mechanical seal is replaced due to a minute leak of a working fluid. It comes under Preventive maintenance.
- If the pump is allowed to run for a long time, it results in the flushing of working fluid due to the complete failure of a mechanical seal. It comes under Breakdown Maintenance.