Table of Contents
Interview Questions Part 2 (6 to 10)
6. What is the physical significance of nodes in the shaft?
A node represents a point of zero displacement (i.e., stationary) in a vibrating wave. These nodal points are the best-suited locations for mounting the bearings on the rotating shaft so that the bearing will be saved from vibratory loads.
For example,
Let us assume a shaft is rotating at a particular frequency f, which corresponds to its first natural frequency then the shaft will vibrate as shown in the following figure.
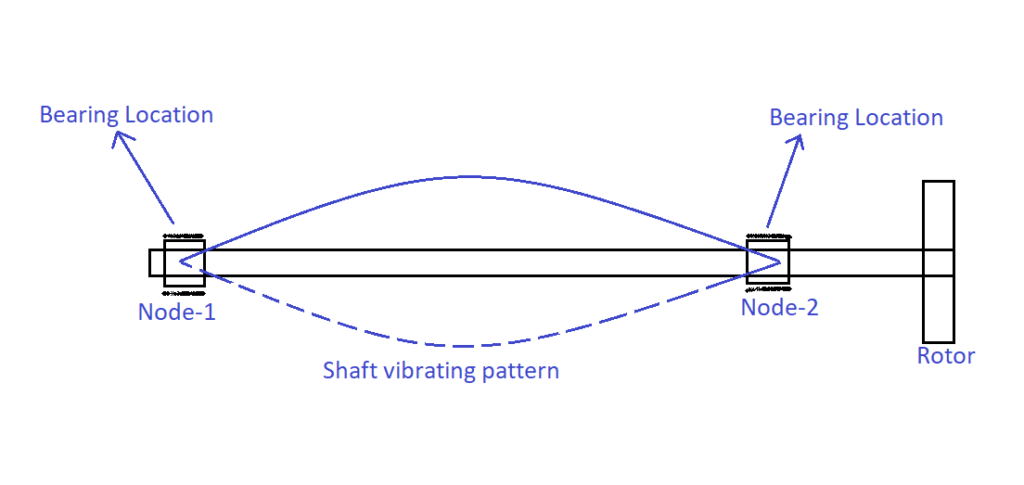
The nodal points are chosen as the bearing locations.
7. Why 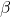 phase is not found in the iron-iron carbide equilibrium phase diagram?
phase is not found in the iron-iron carbide equilibrium phase diagram?
![]() are the sequel Greek alphabets like A, B, and C in English. Temperature above 760
are the sequel Greek alphabets like A, B, and C in English. Temperature above 760 ![]() steel loses its magnetic property i.e., it becomes demagnetised. In earlier days, there was a misconception that the loss of magnetic property upon heating is due to phase transformation from
steel loses its magnetic property i.e., it becomes demagnetised. In earlier days, there was a misconception that the loss of magnetic property upon heating is due to phase transformation from ![]() to a new phase. The new phase was named as
to a new phase. The new phase was named as ![]() . But in later stages, it was revealed that there is no relation between phase transformation and loss of magnetism.
. But in later stages, it was revealed that there is no relation between phase transformation and loss of magnetism.
8. Why maximum carbon content in the iron-iron carbide equilibrium phase diagram is 6.67 % only?
By keep on adding carbon to the iron results in the formation of iron carbide compound ![]() . At 6.67 % of carbon, iron carbide will be in the cementite phase.
. At 6.67 % of carbon, iron carbide will be in the cementite phase.
The atomic mass of iron element = 55.8 amu
The atomic mass of carbon element = 12 amu
So total mass of ![]() compound = 179.4 amu
compound = 179.4 amu
Carbon percentage in ![]() compound =
compound = ![]() =6.67 %
=6.67 %
Thus, it indicates the maximum solubility of carbon in ![]() compound is 6.67%. Generally, carbon is added to the iron when the iron is in the molten liquid state. Beyond 6.67 %, carbon will not get dissolved in
compound is 6.67%. Generally, carbon is added to the iron when the iron is in the molten liquid state. Beyond 6.67 %, carbon will not get dissolved in ![]() compound and it simply floats on the surface due to lower density as compared to
compound and it simply floats on the surface due to lower density as compared to ![]() . Thus, the equilibrium phase diagram does not represent any significant change in carbon addition beyond 6.67%.
. Thus, the equilibrium phase diagram does not represent any significant change in carbon addition beyond 6.67%.
9. Why copper is predominantly used as a tubing material in refrigerators and air conditioners?
Interview Tip: When an interviewer asks a question, try to answer it in different aspects as shown below.
Corrosion Aspect:
Copper is one of the noble metals which resists corrosion by the formation of a protective layer on the surface due to oxidation of copper. The following table represents the thermal conductivity of metals on a rank basis.
Thermal Conductivity Aspect:

According to Fourier’s law of heat conduction, rate of heat transfer ![]() or heat transfer in hallow cylinders
or heat transfer in hallow cylinders ![]() higher the thermal conductivity, higher will be the rate of heat transfer. So, for the same heat transfer rate, copper tubes are in compact size as compared to tubes made of steel and gold.
higher the thermal conductivity, higher will be the rate of heat transfer. So, for the same heat transfer rate, copper tubes are in compact size as compared to tubes made of steel and gold.
Fabrication Aspect:
Copper tubes can be joined easily by using the soldering technique with fewer joining defects as compared to welding because soldering temperatures are relatively lower compared to welding temperatures.
Copper tubes can be bent easily by hand or using a blow torch because of their ductility.
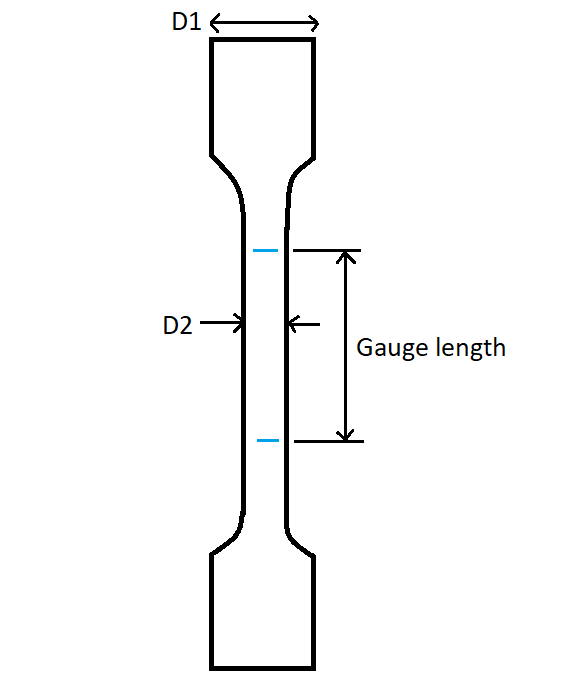
10. Why there are two yield points i.e., upper and lower yield points in the stress vs strain curve of mild steel?
When the dog bone-shaped specimen is subjected to a tension test in Universal Testing Machine as shown in the following figure, the specimen expands in a longitudinal direction i.e., Y direction and contracts laterally in the X- direction.
Because of this lateral contraction, an intense stress field is created (as shown in the following figure) and it causes the interstitial atoms like Boron, Carbon, and Nitrogen difficult to stay there. Hence, these elements diffuse to the locations where free space is available. The location below the dislocation plane is one of the stress-free zones as shown in the following figure.
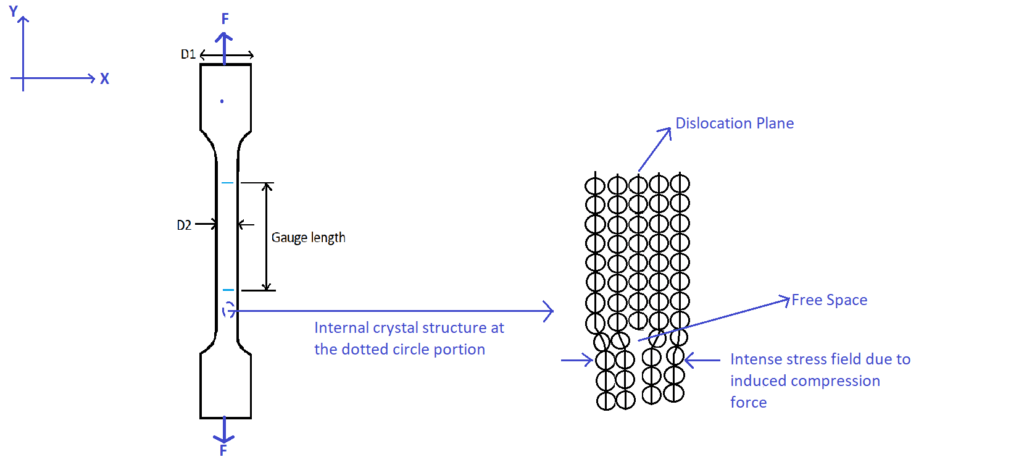
Thus, all the interstitial atoms in the intense stress field diffuse to the bottom of the dislocation plane. It results in the formation of a cluster of interstitial atoms that blocks the movement of the dislocation plane (expansion of material under tension load is due to movement of dislocation plane at the crystal level). Thus, the dislocation plane needs more force to overcome the obstruction. It results in an upper yield point in the stress vs strain curve. Once the dislocation plane crosses the cluster, there is no further hindrance thus, it results in a lower yield point.

