Table of Contents
Interview Questions Part-1 (1 to 5)
1. While plotting stress vs strain curve, which one is input to the specimen? stress or strain?
Strain rate or strain is the input to the specimen. Stress is the measured output. Always input is an independent variable and output is a dependent variable that depends on the given input. Y=F(X), where X is the independent variable and Y is the dependent variable. Therefore, strain is plotted on X-axis and stress is plotted on Y-axis.
2. How the stress vs strain curve is drawn?
- The uni-axial tensile test has to be carried out on a dog bone shaped cylindrical specimen with a non-uniform diameter as shown in the following figure.
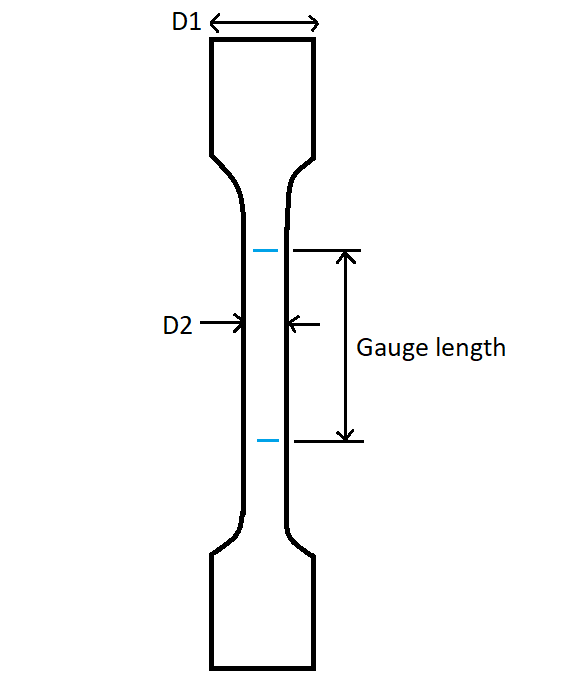
- Two gauge marks have to be marked on the specimen (blue colour lines as shown in the figure) as a reference. Measure the distance between them and assume it as a gauge length.
- Mount the specimen between the jaws of a universal testing machine (UTM). One of the jaws is fixed and another one is movable.
- Displacement at a fixed rate (i.e, mm/s) is given to the movable jaw. Then the distance between two marked lines increases.
- Correspondingly force or load induced on the specimen is measured with the help of load cell attached to the UTM.
- Since displacement is given at a constant rate, it can be considered as a displacement (mm) itself. Now plot the displacement value on X-axis and load value on Y-axis.
- Continue the test until the specimen fails.
- Load vs displacement figure (figure drawn up to elastic limit only for understanding purpose) will be as shown in the following figure.
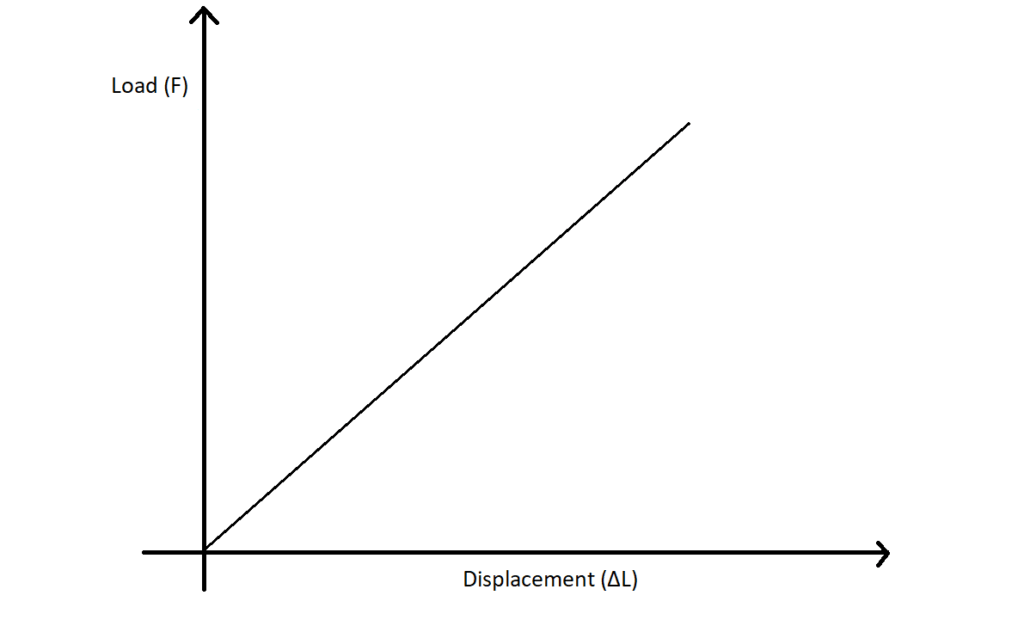
- But if the dimensions of the specimen change like increasing or decreasing the values of diameter and length of the specimen, the plot load vs displacement changes even though the material composition is same.
- So to create a plot that is independent of the dimensions of the specimen, the X-axis variable i.e., displacement is normalized with respect to the gauge length of the specimen as
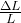 . it means a change in length per unit length, so whatever may the gauge length of the specimen, it is considered as a unit length when displacement is normalized. The normalized ratio
. it means a change in length per unit length, so whatever may the gauge length of the specimen, it is considered as a unit length when displacement is normalized. The normalized ratio 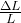 is called strain.
is called strain. - Similarly, the Y-axis variable is normalized with respect to the area near the gauge marks (corresponds to diameter D2) as
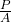 ( where P is the load and A is the area). The normalized ratio is called stress.
( where P is the load and A is the area). The normalized ratio is called stress.
3. Why specifically a dog bone-shaped specimen preferred for tensile testing?
Dog bone-shaped specimen is a cylindrical shaped solid rod whose diameter is relatively larger at the ends as compared to the centre portion as shown in figure-1. So, if the diameter is less, the corresponding area will also be less and the stress will be higher at that particular location resulting in a failure. So that, early failure can be ensured at the centre of the specimen but not at the ends.
4.Which steel is preferred among medium carbon steel and high carbon steel to resist more deformation within the elastic limit for the same external load and of same dimensions?
Medium carbon steel and high carbon steel results in the same deformation under the same external load within the elastic limit. It can be seen from the following figure.
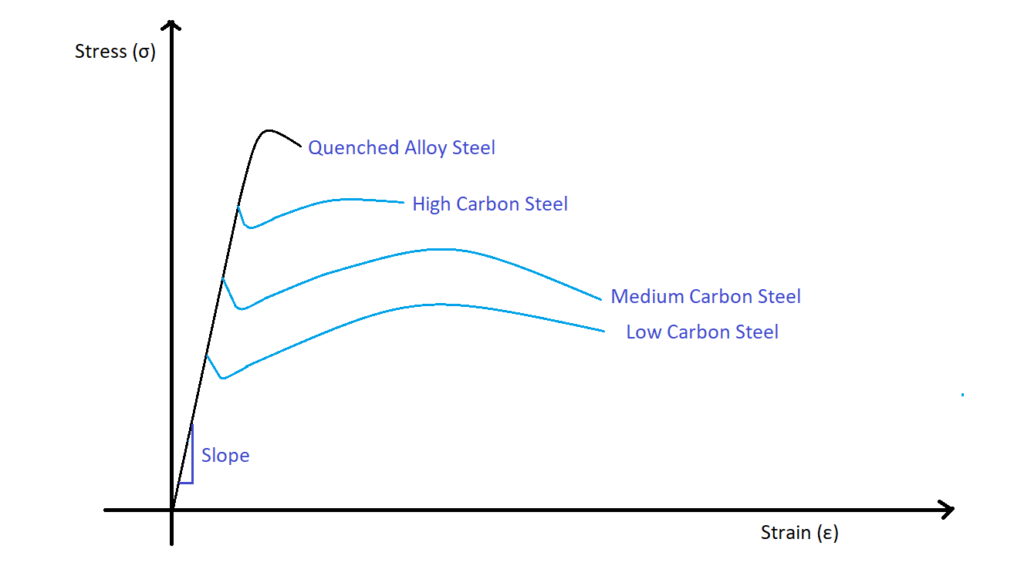
The slope of the stress vs strain curve within the elastic limit represents Young’s Modulus or Elastic modulus (E) as shown in the above figure. Elastic modulus is nothing but resistance to deformation within the elastic limit. Since the slope is same for low, medium and high carbon steel, their resistance to deformation within the elastic limit is same irrespective of their carbon content.
5.Why centrifugal pumps are always started by closing the discharge valve?
Generally, there are three types of centrifugal pumps based on their impeller blade configuration. They are
- Forward Curved Blade
- Radial Blade
- Backward Curved Blade
The shaft power vs flow rate of all the above three fans is shown in the following figure.
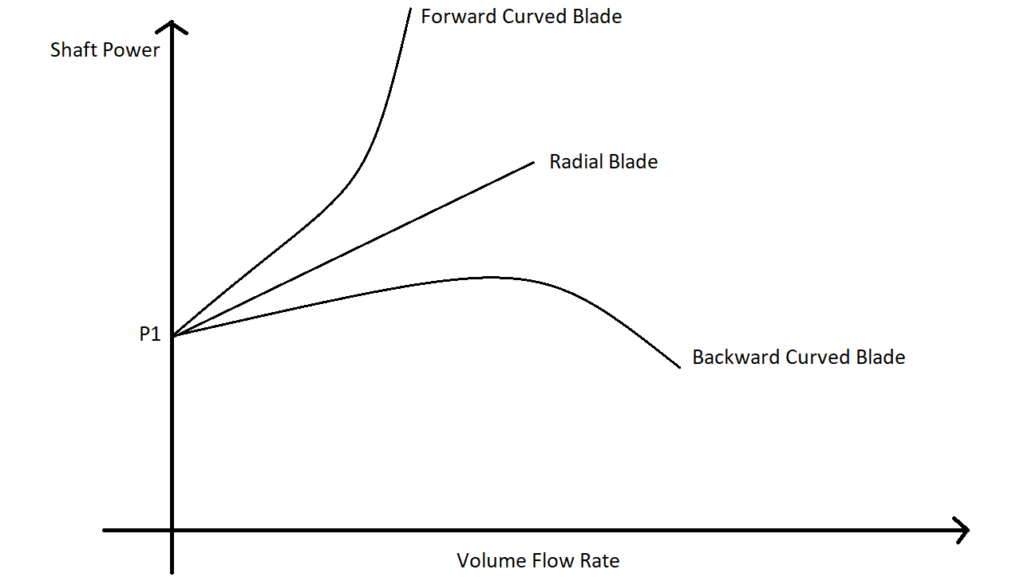
The common thing in all three fans is, the motor consumes the lowest power (P1) when the volume flow rate is zero. Thus, the motor is saved from sudden power surge or overloading by closing the discharge valve. For more details on centrifugal fans visit here.

