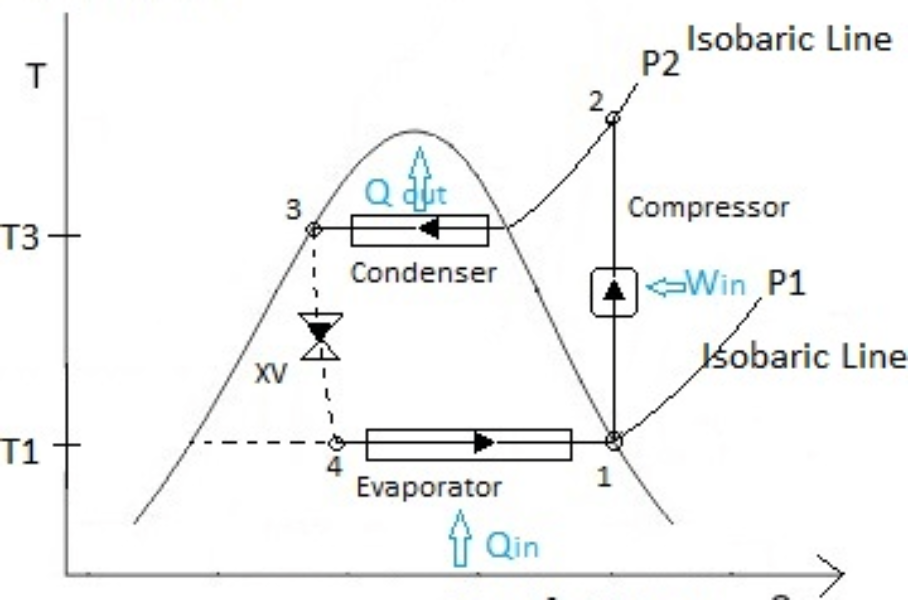
Introduction
Thermodynamic analysis was done on ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle through the following example to evaluate its performance.
A household refrigerator uses R-134a as a refrigerant. It operates on the principle of an ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle. Evaporator pressure is 0.14 MPa and condenser pressure is 0.8 MPa. The mass flow rate of refrigerant in the circuit is 0.05 Kg/s. Find,
-
-
-
Rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space. (Also known as refrigeration capacity)
-
Power input to the compressor.
-
Rate of heat rejected from the condenser.
-
The efficiency of the system (COP Coefficient of Performance)
-
-
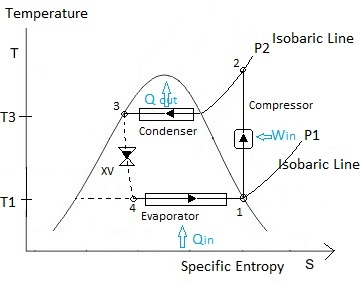
By comparing the given data with the above figure,
P1= P4=0.14 MPa
P2= P3=0.8 MPa
![]()
By observing the question deeply, we can conclude the following things.
-
-
S1=S2 (Since it is ideal refrigeration cycle no losses are expected, thus entropy remain constant between state-1 and state-2 i.e., isentropic compression). S1=Sf @ P1=0.14 MPa=0.944 kJ/kg . K
-
Since throttling is a constant enthalpy process, h3=h4.
-
a. Rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space (![]() or Refrigeration Capacity)
or Refrigeration Capacity)
![]()
h1=hg @ P1=0.14 MPa =239.1 kJ/kg
h4= h3 @ P2=0.8 MPa = 95.4 kJ/kg
By substituting this data in above equation, we get ![]() = 7.185 KW
= 7.185 KW
b. Power input to the compressor (![]() )
)
![]()
From P2= 0.8 MPa, S1=0.944 kJ/kg .K, h2 can be found from the superheated table of R-134a,h2=275.3 kJ/kg
By substituting this data in above equation, we get ![]() =1.81 KW
=1.81 KW
c. Rate of heat rejected from condenser ( ![]() )
)
![]()
By substituting the available data in the above equation, we get ![]() =9.0 KW
=9.0 KW
d. Efficiency of the system, (Coefficient of Performance)
![]()
Conclusion
-
COP = 4 indicates that the refrigerator removes 4 units of thermal energy from the refrigerated space for every 1 unit of electrical energy consumption.
-
Refrigeration capacity (
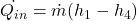 ) can be increased in following ways.
) can be increased in following ways.-
-
Increasing the mass flow rate of refrigerant in the circuit.
-
Increasing the enthalpy h1 by allowing the refrigerant to get superheated in the evaporator itself
-
Reducing the enthalpy h4 by reducing the evaporator pressure further down. It can be achieved by using very low boiling point refrigerants.
-
-
-
Heat rejected from the condenser is more than the heat absorbed from the refrigerated space
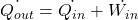 . That’s why opening the fridge door in a closed room will never reduce the room temperature.
. That’s why opening the fridge door in a closed room will never reduce the room temperature. -
For any refrigeration system using R-134a as a refrigerant, always its condenser pressure will be in the range of 0.7 to 0.9 MPa if the condenser cooling water temperature is in the range of 28 to 38 °C.
-
Refrigerant pressure in the evaporator & in the condenser is constant because of its phase change. And one more logic is that there is no restriction to the flow of refrigerant in evaporator & in condenser hence pressure remains constant.