Table of Contents
Introduction
Once the required specifications of a centrifugal pump are finalized by a customer and shared with the supplier for manufacturing, stage-wise testing and inspection of centrifugal pumps are necessary before and after manufacturing the centrifugal pump. The following table represents some of the essential specifications of a centrifugal pump from the manufacturer’s point of view.
SL | Centrifugal Pump’s Specifications | Magnitude/ Type |
1 | pH value of process fluid | ____________ |
2 | The specific gravity of the process fluid | ____________ |
3 | Required flow (m3/hr) (duty point) | ____________ |
4 | Required head (m) (duty point) | ____________ |
5 | Shaft power (KW) at duty point | ____________ |
6 | Efficiency (%) at duty point | ____________ |
7 | Pump Type | Horizontal/ Vertical/ In line |
8 | Impeller Type | Open/ Closed/ Semi-open |
9 | Vane Type | Forward/ Backward/ Radial |
10 | Type of axial thrust balancing for a shaft | Balancing holes/ Back vane type/None |

Testing and Inspection of Centrifugal Pumps Before Manufacturing
Material Test
A material test involves the following two types. They are chemical and mechanical tests.
Chemical Test
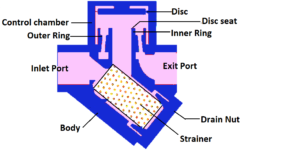
Reviewing the material test certificate by a customer is necessary to judge whether the manufacturer chose the suitable material to manufacture the components of a centrifugal pump by analyzing the chemical composition. Chemical test plays a key role in the testing and inspection of centrifugal pumps. The manufacturer should perform the test according to ASTM or any equivalent standards. The parts in direct contact with process fluid must be inert to avoid wear, tear, and corrosion problems. The following table represents the components in direct contact with the process fluid, i.e., wetted parts.
Sl | Part |
1 | Impeller |
2 | Back-plate |
3 | Casing |
4 | Shaft |
5 | Mechanical Seal / gland packing |
6 | Shaft sleeve |
Mechanical Test
Though the chemical composition of the material reveals the construction material, the mechanical test ensures mechanical properties like yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and hardness. etc. The reference standard for the mechanical testing of steel products is ASTM A370. The following are the essential parameters to be measured while performing the mechanical test.
SL | Parameter | Magnitude |
1 | Yield Strength (Mpa) | |
2 | % Elongation | |
3 | Ultimate Tensile Strength (Mpa) | |
4 | Hardness | |
5 | Location of Fracture |
Testing and Inspection of Centrifugal Pumps After Manufacturing
Ultrasonic Test
It is a non-destructive test (NDT) that is mandatory for rotating parts like a shaft and impeller to check internal flaws like casting defects, internal cracks..etc. The fatigue strength of a rotating component reduces if it contains flaws. Of course, no material can be 100% flawless. So, the customer can follow ASME Section V Article 23 (Acceptance criteria for ultrasonic examination) to reject or accept a material.
Hydrostatic Test
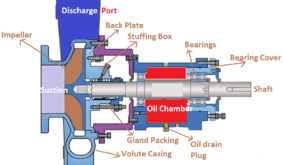
The casing experiences a relatively higher pressure than any other part of the centrifugal pump. A hydrostatic test of the casing is necessary to judge the robustness of the construction. The test ensures structural integrity and checks for cracks and leaks due to defective casting…etc.
Hydrostatic Test Pressure
The reference standard for the centrifugal pump’s casing hydrostatic test is IS 5120, clause 17.6. The test pressure is 1.5 ![]() , the maximum discharge pressure experienced by the casing. In general, centrifugal pumps encounters different suction conditions as follows.
, the maximum discharge pressure experienced by the casing. In general, centrifugal pumps encounters different suction conditions as follows.
Flooded Condition:
Maximum discharge pressure= Maximum inlet pressure + Maximum Developed head by the pump
Suction Lift Condition:
Maximum discharge pressure = Maximum head developed by the pump.
Note: Since it is a suction lift, the inlet pressure due to the gravity of the fluid is zero.
Balancing
The impeller should be free from the static, couple, and dynamic imbalance. Any imbalance in the impeller generates severe vibration at high speeds that can damage the mechanical seals, bending of the shaft, damage bearings, coupling..etc. Before installing the newly fabricated impeller to the pump, checks for imbalance and calculation of residual unbalance present in the impeller is necessary. The residual unbalance in the impeller should be less than the permissible residual unbalances as per balancing standards ISO 1940 grade 6.3.
Dimensional Check
Critical dimensions of the pump like base frame size, the height of the shaft from the pump’s base, suction and discharge flange sizes, bolt holes pitch..etc should be checked from General Arrangement (GA) drawing or detailed drawing of the pump.
Test Plan of a Centrifugal Pump
- Check the oil level in the pump. (Fill the oil up to half the level of the sight glass)
- Ensure sufficient water level in the source tank.
- Open the suction valve and close the discharge valve.
- Start the pump.
- Measure the running speed of the pump using a tachometer.
Hydraulic Performance Test of a Centrifugal Pump
- Measure the developed shut-off head and compare the value with the performance characteristic curve of the given centrifugal pump.
- Check for any leaks from the casing and the mechanical seal.
- Open the discharge valve slowly till the rated flow is achieved and measure the discharge pressure.
- Measure the discharge head & flow rate and compare the same with characteristic curves.
- Measure the power drawn by the motor and compare it with the characteristic curve. (Note: The power shown in the characteristic curve is shaft power. So, shaft power = Power drawn by motor
 Motor Efficiency
Motor Efficiency
Vibration Test
- Measure the vibration of the pump & motor and record it in the following format.
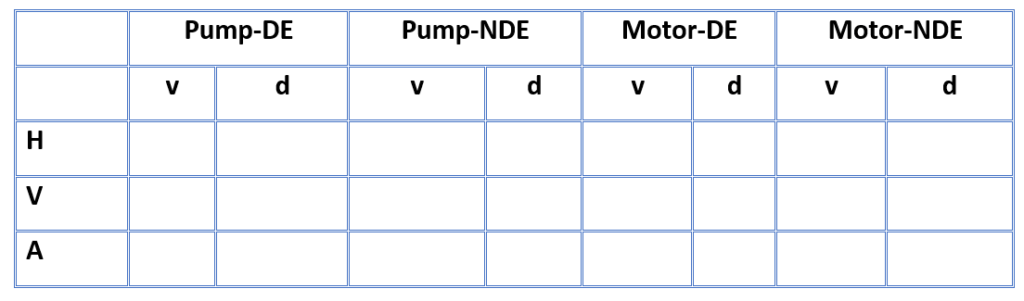
Note: The reference standard for vibration measurement of a centrifugal pump is ISO 10816 Part-7
DE: Stands for Drive-End
NDE: Stands for Non-Drive End
v: Stands for Root Mean Square (RMS) vibration velocity in mm/s
d: Stands for peak-to-peak displacement in microns
The Following represents the mounting direction of the accelerometer probe on the rotating machinery.
H: Stands for the horizontal direction
V: Stands for the vertical direction
A: Stands for axial direction
Vibration reveals any unbalance, misalignment, and incorrect bearing mounting present in the pump.
Noise Test
Measure the noise level of the pump using the sound level meter. The maximum acceptable value is 90 dB (A) measured at a distance of 1 meter away from the running pump.
Note:
ISO 9906 is a widely followed hydraulic performance test for customers’ acceptance of rotodynamic pumps including centrifugal, axial, and mixed pumps.
Why ISO 9906 is required?
The pump is an assembly of different components. Errors are inevitable while manufacturing. When all the components are assembled to make a pump, the accumulated error of all the parts leads to a specific deviation in the pump’s performance. Then the standard ISO 9906 comes into the picture suggesting the customers to accept or reject a pump by providing acceptable tolerance in the pump’s performance i.e., acceptable tolerance band on flow rate, head developed..etc.
ISO 9906 consists of three different grades based on acceptable tolerance on the pump’s performance parameters.
Reference Standards for Various Tests of Centrifugal Pump
SL | Test | Reference Standard |
1 | Mechanical testing of steel products | ASTM A370 |
2 | Chemical Composition Test | Equivalent ASME Standards |
3 | Acceptance criteria for ultrasonic examination | ASME Section V Article 23 |
4 | Hydrostatic Test | IS: 5120, clause 17.6 |
5 | Balancing | |
6 | Vibration | ISO 10816 Part-7 |
7 | Hydraulic Performance | IS 9906 |