Table of Contents
Introduction to Teflon (aka) PTFE
Teflon is a trademark given by the Dupont company for the chemical compound they developed called polytetrafluoroethylene in short PTFE. The chemical structure of PTFE is shown in the following figure.
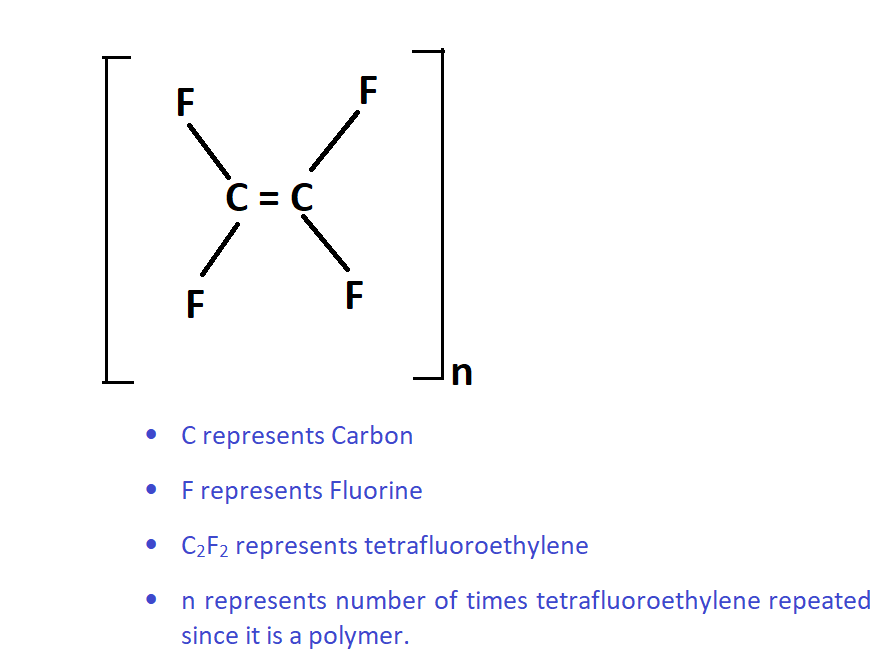
Poly means “many” tetra means “four” atoms fluoro means “Fluorine atom ethylene bears the structural formula C2H2 in general. But Hydrogen atoms area replaced with fluorine atoms as shown in the above figure.
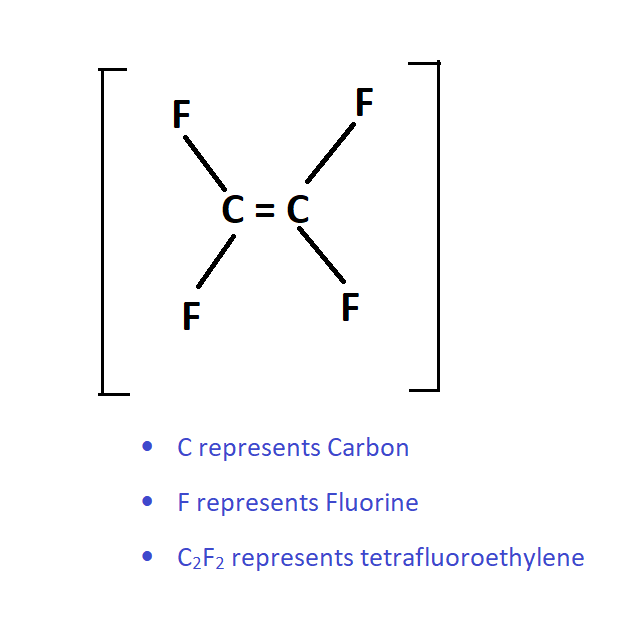
Monomer of Teflon/PTFE
Mono means “single”. The structure C2F2 repeats only once as shown in following figure.
Properties and Characteristics of PTFE (aka) TEFLON
Property-1: PTFE is non-reactive or inert to most of the chemicals
Characteristic: Bonding between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest single bonds. In general, fluorine is the most electronegative element in the periodic table. Therefore, it repels all the other atoms thus making it inert and non-reactive to most of the chemicals. Fluorine atoms surround the carbon atoms in such a way that any other atom cannot react with the carbon atom also.
Application: Gaskets made of PTFE are used for joining the pipe fittings in chemical processing industry.
Property-2: Non-sticky or Hydrophobic
Characteristic: Due to high electronegativity, materials in contact will get repelled without getting adhered to the surface.
Application: PTFE coated on cooking wares like pans to avoid sticking of vegetables when they are roasted. The only surface on which a gecko (a kind of lizard) cannot stick is PTFE.
Property-3: Low coefficient of friction or Solid lubricant
Characteristic: Electronegativity and non-sticky characteristic lead to a low coefficient of friction and the value is around 0.05 to 0.10. Therefore, PTFE can be used as a solid lubricant. PTFE against stainless is one of the lowest coefficients of friction between any two solids.
Application: Simple sliding PTFE bearings between structure and substructure of bridges, PTFE piston rings ensure perfect sealing and avoid friction between the piston and its cylindrical casing, the lining of pipelines for powder transfer system.
Property-4: Non-flammable
Characteristic: Fluorine and other elements in its column of the periodic table (i.e, halogen) have high flame retardancy due to high oxygen index (Oxygen index represents the amount of oxygen needed to support the flame combustion).
Application: Electric wire insulations.
Property-5: Wide Operational Temperature Range
Melting point = 327 ![]()
Chemical decomposition point = 200 ![]()
Can be used at cryogenic temperatures (up to – 250 ![]() ) also without losing much of its mechanical properties.
) also without losing much of its mechanical properties.
Property-6: Reaction with alkali elements
The alkali elements like Cesium, Francium, Potassium, Sodium…etc. are the only elements that react with PTFE.
Manufacturing Method of Teflon
PTFE is a thermoplastic polymer. On heating it will melt down but liquid PFTE will have very high viscosity which is difficult to produce the various shapes like as of casting. Various materials made of PTFE is produced through powder metallurgy route.
Conclusion
Features of PTFE
- Chemical inertness
- Non-sticky
- Dry solid lubricant
- Hydrophobic
- Non-flammable
- Low coefficient of friction
- Low resistance to creep
- Suitable functional temperature range (-250
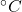 to + 200
to + 200 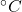 )
)