Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email.
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
What are the types of unbalances?
Unbalance in rigid rotating systems is classified into three types based on the relative position of the axis of rotation (i.e., shaft axis) and axis of centre of mass (i.e., center of gravity) of rotating rigid rotor. They are Figure 4: Figure represents the types of unbalances in rigid rotating syRead more
Unbalance in rigid rotating systems is classified into three types based on the relative position of the axis of rotation (i.e., shaft axis) and axis of centre of mass (i.e., center of gravity) of rotating rigid rotor. They are
Figure 4: Figure represents the types of unbalances in rigid rotating system
Follow the link for further reading: Balancing of Rigid Rotating Systems – The Mechanical Engineer (amechieneer.com)
See lessWhat is mechanical vibration?
In short, it is the vibration of rotating or reciprocating mechanical components. Every rotating and reciprocating component operating at certain speed generates vibration which is inevitable. Of course, we cannot see the high frequency vibrations visually, but we can feel it and measure it throughRead more
In short, it is the vibration of rotating or reciprocating mechanical components. Every rotating and reciprocating component operating at certain speed generates vibration which is inevitable. Of course, we cannot see the high frequency vibrations visually, but we can feel it and measure it through vibration sensors.
See lessHow to differentiate rotating element looseness and structural looseness from the vibration spectrum?
Rotating element looseness includes looseness in bearings, gears, couplings …etc and the vibration signal characteristic is as follows. Significant vibration amplitude in radial directions as compared to axial. Multiple harmonics from 1 $\times \,$ RPM to 10 $\times \,$ RPM.
Rotating element looseness includes looseness in bearings, gears, couplings …etc and the vibration signal characteristic is as follows.
- Significant vibration amplitude in radial directions as compared to axial.
- Multiple harmonics from 1
 RPM to 10
RPM to 10  RPM.
RPM.
See lessWhat is the source of mechanical looseness?
Mechanical looseness in the sense, improper contact between adjacent components. Mechanical looseness can occur due to following reasons. Improper tightening of bolts. Wear and tear of components Fracture in the component.
Mechanical looseness in the sense, improper contact between adjacent components. Mechanical looseness can occur due to following reasons.
- Improper tightening of bolts.
- Wear and tear of components
- Fracture in the component.
See lessWhat are the vibration characteristics of mechanical looseness?
The time period waveform is erratic and pattern is non repetitive. Frequency spectrum displays multiple harmonics 1 to 10 $\times \, $RPM, sub harmonics 0.5$\times \, $ RPM and half harmonic 1.5, 2.5, 3.5 $\times \,$ RPM. Some driving force is required for looseness. Mechanical looseness get aggraRead more
The time period waveform is erratic and pattern is non repetitive.
Frequency spectrum displays multiple harmonics 1 to 10 RPM, sub harmonics 0.5
RPM, sub harmonics 0.5 RPM and half harmonic 1.5, 2.5, 3.5
RPM and half harmonic 1.5, 2.5, 3.5 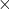 RPM.
RPM.
Some driving force is required for looseness. Mechanical looseness get aggravated in presence of driving force like unbalance…etc.
See lessHow to calculate the permissible residual unbalance?
Permissible residual unbalance of a rotor can be found by two ways. They are Way-1 Using Direct Relation Permissible residual unbalance can be found using following relation. $ U_{Per}= 1000 \times \, \frac{G \, m}{\omega} $ Where $ U_{Per} $ represents Maximum Permissible Residual Unbalance in a roRead more
Permissible residual unbalance of a rotor can be found by two ways. They are
Way-1 Using Direct Relation
Permissible residual unbalance can be found using following relation.
Where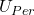 represents Maximum Permissible Residual Unbalance in a rotor.
represents Maximum Permissible Residual Unbalance in a rotor.
G represents the balancing quality grade. G is selected based on the application. For example, G 6.3 is used for the rotors of fans and pumps.
m represents the rotor mass.
Way-2 Using Graph
Permissible residual unbalance can be calculated using following graph as well.
Let us consider, you have to determine the permissible residual unbalance for a centrifugal pump rotor (G 6.3) of mass (m) with a service speed of 2000 RPM, then Specific Permissible Residual Unbalance can be determined from the following graph.
Figure 3: Graph represents the permissible residual unbalance.
Select the speed in X-axis (2000 RPM) and draw a vertical line that intersects the balance quality grade line G 6.3. From here draw a horizontal line that intersects Y- axis. The corresponding value in Y axis represents the
See less