Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email.
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
What is intergranular corrosion?
When the austenitic stainless steel is heated in the range from 500 to 850 $^o C \, $ and allowed to cool slowly [i.e welding the austenitic stainless steel and allowing it to cool in the air], the carbon in the grains diffuses to the is grain boundary. Because the diffusivity of carbon is greater tRead more
When the austenitic stainless steel is heated in the range from 500 to 850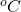 and allowed to cool slowly [i.e welding the austenitic stainless steel and allowing it to cool in the air], the carbon in the grains diffuses to the is grain boundary. Because the diffusivity of carbon is greater than chromium at high temperatures. This is due to the size of carbon is half the size of chromium. Hence carbon diffuses faster. The carbon combines with chromium and forms chromium carbide. Thus, chromium is not available in the grain boundary to form an inert layer called chromium oxide. And also, the chromium layer carbide in the grain boundary acts as a narrow anodic zone and the grains rich in chromium act as a cathodic zone. It results in galvanic coupling and leads to the corrosion between grains i.e., in the grain boundary called inter-granular corrosion.
and allowed to cool slowly [i.e welding the austenitic stainless steel and allowing it to cool in the air], the carbon in the grains diffuses to the is grain boundary. Because the diffusivity of carbon is greater than chromium at high temperatures. This is due to the size of carbon is half the size of chromium. Hence carbon diffuses faster. The carbon combines with chromium and forms chromium carbide. Thus, chromium is not available in the grain boundary to form an inert layer called chromium oxide. And also, the chromium layer carbide in the grain boundary acts as a narrow anodic zone and the grains rich in chromium act as a cathodic zone. It results in galvanic coupling and leads to the corrosion between grains i.e., in the grain boundary called inter-granular corrosion.
See lessWhat is predictive maintenance?
Predicting the future of equipment and preventing it from catastrophic failure based on the present condition of the equipment is called predictive maintenance. The present condition of the equipment is monitored using condition-monitoring techniques like vibration, noise, temperature…etc. DevelopinRead more
Predicting the future of equipment and preventing it from catastrophic failure based on the present condition of the equipment is called predictive maintenance. The present condition of the equipment is monitored using condition-monitoring techniques like vibration, noise, temperature…etc. Developing faults can be identified by measuring and trending the vibration. The root cause of the fault can be detected by performing a frequency analysis of the vibration.
See lessWhat is bearing life?
The bearing life of an anti-friction bearing is defined as the number of revolutions (in millions) or the number of hours at a given speed that 90% of bearings in a lot will withstand before the signs of the first failure.
The bearing life of an anti-friction bearing is defined as the number of revolutions (in millions) or the number of hours at a given speed that 90% of bearings in a lot will withstand before the signs of the first failure.
See lessWhy measuring the vibration of a machine is important?
In general, the vibration of rotating or reciprocating equipment under operation (pumps, compressors…etc.) obeys the following governing differential equation of motion M\ddot{x}+C\dot{x}+Kx=F_{Exciting \, Force}. The LHS of the equation represents the sum of the inertia force, damping force and sprRead more
In general, the vibration of rotating or reciprocating equipment under operation (pumps, compressors…etc.) obeys the following governing differential equation of motion M\ddot{x}+C\dot{x}+Kx=F_{Exciting \, Force}. The LHS of the equation represents the sum of the inertia force, damping force and spring force of the equipment. The RHS of the equation represents the excitation force due to faults in the running equipment. Faults like unbalance in the impeller, misalignment between motor and the pump, structural looseness, bearing failure, cavitation & flow turbulence in case of centrifugal pumps..etc induce F_{Excitation \, Force}. If RHS is greater than LHS, i.e. the magnitude of the exciting force is greater than the restoring force of the equipment, then the equipment is subjected to significant vibration. By analysing the frequency and the magnitude of the F_{Exciting \, Force}, the source of fault can be identified. Hence measuring the vibration of equipment indicates its health condition. By analysing the vibration, the incipient faults can be identified and equipment can be saved from a catastrophic failure.
See lessHow do you measure vibration?
Vibration is measured in terms of displacement, velocity and acceleration. Vibration is defined as to and fro motion of an object from its equilibrium or means position as shown in the following figure. The distance travelled by an object between the mean position and the extreme position is calledRead more
Vibration is measured in terms of displacement, velocity and acceleration. Vibration is defined as to and fro motion of an object from its equilibrium or means position as shown in the following figure. The distance travelled by an object between the mean position and the extreme position is called displacement and similarly, the distance travelled between the extreme left and extreme right position (with respect to the following figure) is called peak displacement. The velocity of an object is zero at its extreme positions and maximum at the mean position. Since velocity is changing with respect to the position, average velocity or Root Mean Squared (RMS) velocity is preferred. Sometimes peak velocity is also used. Since an object changes the direction of motion at its extreme positions, the acceleration is maximum at the extreme positions and zero at the mean position. Since acceleration also changes with respect to the position of an object, average acceleration or Root Mean Squared (RMS) acceleration is preferred.
Figure: Spring mass sytem
See lessWhat is vibration?
Vibration is defined as to and fro motion of an object from its mean equilibrium position. The oscillation of an object is also similar to vibration but with a relatively low frequency and relatively high amplitude (displacement). Whereas the vibration of an object has low amplitude (displacement) aRead more
Vibration is defined as to and fro motion of an object from its mean equilibrium position. The oscillation of an object is also similar to vibration but with a relatively low frequency and relatively high amplitude (displacement). Whereas the vibration of an object has low amplitude (displacement) and high frequency. Ex. The motion of a simple pendulum is defined as oscillation but not as vibration.
See lessWhy mechanical seal is called mechanical?
Mechanical seal uses mechanical components like spring, screws, spring retainer and seal faces to seal the gap between rotary (shaft) and stationary portion (housing) of a pump. Mechanical seal contains stationary face and rotary face combination to create the seal. The rotary and stationary faces aRead more
Mechanical seal uses mechanical components like spring, screws, spring retainer and seal faces to seal the gap between rotary (shaft) and stationary portion (housing) of a pump. Mechanical seal contains stationary face and rotary face combination to create the seal. The rotary and stationary faces are pressed against each other with the help of mechanical spring to achieve the seal. Hence it is called mechanical seal. It is in contrast to other types of seals like gland packing and lip seals where sealing is achieved by means of non-mechanical things. the gland ropes are just braided ropes wrapped around the shaft of the pump to seal the gap between shaft and the housing.
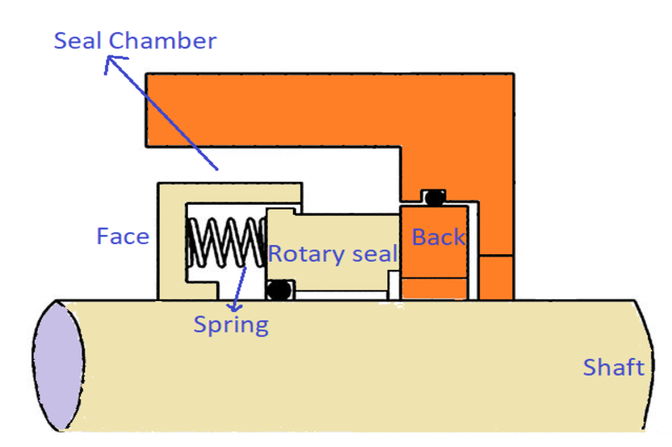
See lessWhy internal clearance is given in bearing?
There are two reasons why internal clearance in the bearing is necessary. Reason: -1 Due to interference fit between the bearing outer race and the housing, the outer race tries to shrink a little. Similarly, the interference fit between the shaft and the inner race, the inner race tries to expand aRead more
There are two reasons why internal clearance in the bearing is necessary.
Reason: -1 Due to interference fit between the bearing outer race and the housing, the outer race tries to shrink a little. Similarly, the interference fit between the shaft and the inner race, the inner race tries to expand a little. To accommodate the shrink and expansion of bearing races, internal clearances in the bearing are necessary.
Reason: -2 During operation due to friction between bearing components, internal clearances are required to accommodate the differential thermal expansion of bearing components.
See lessWhat is the internal clearance code for bearing?
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) established five classes of bearing clearances. They are ISO Clearance Classes Internal Clearance Group-2 Smaller than normal clearance Group-N (Normal) Normal clearance Group-3 Greater than normal clearance Group-4 Clearance greater than group-3Read more
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) established five classes of bearing clearances. They are
Apart from this, manufacturers had established their own designation for bearing clearance in form of suffixes like 6205 C3.
What is the difference between the open-ended and closed-ended rotor of a Rotary Air Lock Valve?
Open Ended Rotor Close Ended Rotor Construction: Rotor does not contain end plates. The rotor contains shaft and vanes only. Construction: Rotor contains end plates at both ends along with the shaft and the vanes. Application: Since there are no end plates, the abrasive material will wear the casingRead more
Figure:- Open Ended Rotor
Figure:- Closed End Rotor
See less